Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer: Key Findings Revealed
Bile imbalance and liver cancer have become critical topics in understanding liver health, particularly in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Recent research highlights the crucial role bile acids play, as they not only aid in fat digestion but also influence various metabolic processes that can lead to serious liver disease. Disruption of bile acid regulation has been identified as a significant risk factor for liver injury and inflammation, paving the way for cancer development. The YAP-FXR relationship emerges as a pivotal molecular switch, demonstrating how YAP’s repressive action on the FXR receptor can trigger liver cancer progression. With insights from studies on liver cancer causes, these developments offer new avenues for liver disease treatment, promising improvements in patient outcomes.
When we discuss bile imbalance and liver cancer, we also delve into the broader realm of liver health issues and neoplastic conditions affecting this vital organ. The intricate relationship between bile acids, their metabolism, and hepatic diseases showcases the gravity of hormonal influences on liver function and growth. Hepatocellular carcinoma, marked as a leading cause of cancer-related morbidity, underscores the necessity of understanding the mechanisms that contribute to its emergence, particularly through disrupted bile acid homeostasis. As research uncovers the complex interplay between signaling pathways—especially involving YAP and FXR—the potential for innovative therapeutic approaches arises, demonstrating the need for ongoing exploration in liver disease treatment. By focusing on bile as a crucial factor in liver pathology, we can illuminate the path to better management strategies.
Understanding the Role of Bile Acids in Liver Health
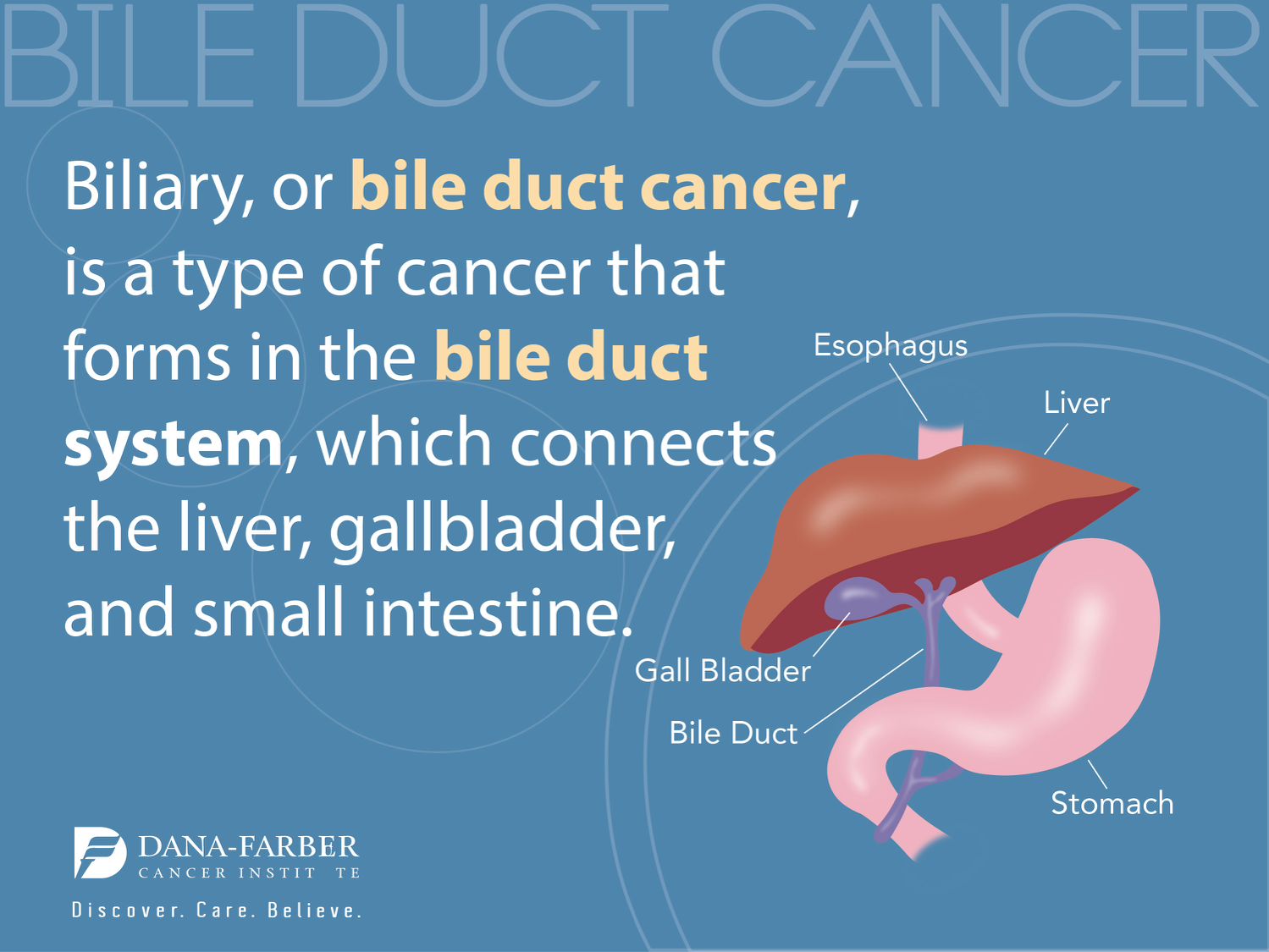
Bile acids are crucial elements produced by the liver, playing an essential role in digestion and metabolism. They facilitate the emulsification of dietary fats, aiding in their absorption in the intestine. Aside from their digestive functions, bile acids also have significant roles in metabolic regulation, affecting how the body processes nutrients and maintains homeostasis. When the balance of bile acids is disrupted—often due to liver disease—this can lead to severe consequences, including inflammation and fibrosis, which may ultimately escalate to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer.
Research has shown that an imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver injury and promote cancer development. For instance, an increase in bile acids can lead to toxic accumulation within liver cells, causing cellular stress and damage. This cascade of events not only contributes to liver disease but also enhances the risk of developing cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Scientists are actively investigating how this bile imbalance may affect the liver’s overall function and its capacity to ward off diseases.
The Connection Between Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
The link between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer is becoming increasingly evident in scientific research. One of the pivotal findings is that an excess of bile acids can lead to the activation of oncogenic pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway. Normally, this pathway plays a crucial role in controlling cell growth and tissue development. However, disruptions caused by an imbalance in bile acids can lead to aberrant signaling that promotes the proliferation of cancerous liver cells.
A study revealed that when YAP—a key protein in the Hippo pathway—is overactivated due to bile acid dysregulation, it represses the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR). This dysfunction results in further bile acid accumulation, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and fibrosis that predisposes the liver to cancer. By restoring the balance of bile acids or enhancing FXR function, there is potential to halt this progression, highlighting the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis in preventing liver cancer.
Insights into YAP and FXR: Key Players in Liver Disease
The dynamic between YAP and FXR is critical in understanding liver disease’s underlying mechanisms. YAP is known for its role in promoting tumor growth; however, its interaction with bile acid metabolism presents a complex picture. In healthy liver function, FXR regulates bile acid levels, ensuring they remain within a safe range. But when YAP is activated by bile acid accumulation, it alters FXR’s effectiveness, leading to increased levels of bile acids that can cause further liver damage.
Understanding this relationship opens new doors for liver disease treatment. By focusing on the inhibition of YAP’s repressive function on FXR, researchers could develop therapies that restore the balance of bile acids within the liver. Potential pharmacological interventions may include drugs aimed at enhancing FXR activity or promoting the excretion of excess bile acids, both of which could significantly diminish the risk of liver cancer progression.
Research Advancements in Liver Disease and Cancer
Recent studies have revealed substantial insights into liver disease and cancer, particularly focusing on the roles of bile acids and related signaling pathways. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms that govern liver function and its responses to bile acid imbalances, new therapeutic targets are emerging. For instance, treatments that effectively enhance FXR activity may represent a promising avenue for mitigating liver damage and preventing the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma.
These advancements are essential not just for understanding liver cancer causes but also for developing comprehensive treatment plans that target the molecular pathways involved in liver disease. As this research evolves, it may also uncover broader implications for understanding metabolic diseases linked to bile acid dysregulation, marking an exciting frontier in hepatology.
The Future of Liver Cancer Treatment
As researchers continue to elucidate the complexities of liver disease and its connection to bile imbalance, the future of liver cancer treatment looks promising. Strategies that focus on rectifying bile acid dysregulation and targeting specific molecular pathways, like the Hippo/YAP axis, could lead to novel therapeutic interventions. This shift towards personalized medicine, tailored to the intricacies of an individual’s liver metabolism and cancer progression, marks a significant progression in oncological research.
Moreover, innovative pharmacological solutions aimed at enhancing the function of FXR may not only alleviate liver damage but could also serve as a preventative measure against the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Continuous support from institutions like the National Institutes of Health is vital in driving forward this promising research, ensuring that new insights translate into effective treatments for patients suffering from liver diseases.
Bile Acids: A Double-Edged Sword
While bile acids are essential for digestion and metabolic processes, elevated levels can act as a double-edged sword. On one hand, they are necessary for the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins; on the other hand, an excess can lead to toxicity and liver injury. Understanding this dual role is crucial for developing strategies aimed at balancing bile acid levels, preventing liver disease, and minimizing the risk of liver cancer.
Research has shown that managing bile acid concentrations can significantly impact liver health. By regulating levels through dietary adjustments, pharmacological interventions, or lifestyle changes, individuals may reduce their risk of developing liver-related conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Continued research in this area is fundamental in uncovering the full potential of bile acids as both therapeutic agents and contributors to liver pathology.
Implications of Bile Acid Regulation on Overall Health
The regulation of bile acids extends beyond liver health, influencing overall metabolic functions in the body. Bile acids are involved in the modulation of glucose metabolism, lipid homeostasis, and even inflammation. Therefore, an imbalance in bile acids can cause widespread effects not only on liver function but also on systemic health, emphasizing the need for comprehensive approaches to address bile acid dysregulation.
Recognizing the interplay between bile acids and various bodily systems could pave the way for preventative health strategies. By implementing lifestyle changes that promote bile acid balance—such as diet and exercise—individuals may experience improvements not only in liver health but also in their overall metabolic efficiency. These insights highlight the significance of bile acids in holistic health management.
Innovative Approaches to Bile Management in Liver Disease
As understanding of bile acid roles in liver pathology evolves, so too do innovative approaches to managing bile acid levels in patients with liver disease. Therapies that promote the secretion of bile acids or enhance the liver’s capacity to process them can be cornerstones in treatment paradigms aimed at preventing hepatocellular carcinoma. Such strategies require robust research and clinical trials to assess their effectiveness and safety in diverse patient populations.
Furthermore, adopting a multifaceted treatment approach may yield the best outcomes for individuals with compromised liver function. By combining dietary management, pharmacological interventions, and lifestyle modifications, there is potential not only to treat existing conditions but also to prevent the development of diseases such as liver cancer. Collaborative research efforts are essential to bring these innovative ideas into clinical practice.
Collaboration in Liver Research: A Multidisciplinary Effort
Addressing the complexities of liver diseases and their connection to bile acid dysregulation demands a multidisciplinary research approach. Collaboration between hepatologists, molecular biologists, and pharmacologists is crucial for uncovering the intricate mechanisms that lead to liver cancer. By combining expertise from various fields, more comprehensive and effective treatment strategies can be developed.
Participating in networks such as the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center allows for the sharing of knowledge and resources, enhancing the research capabilities of each individual entity focused on liver disease. This collaborative spirit will be instrumental in translating research findings into real-world applications, ultimately improving patient outcomes in liver health and cancer management.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance linked to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance occurs when the production and regulation of bile acids are disrupted. This can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. When bile acids accumulate in the liver, they contribute to fibrosis, inflammation, and ultimately tumor formation.
What are the causes of liver cancer and how does bile imbalance play a role?
Liver cancer can be caused by various factors, including chronic liver disease, hepatitis infections, and bile imbalance. Disruption in bile acid metabolism affects liver health, leading to conditions like liver inflammation and fibrosis, which can progress to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What is the relationship between YAP and bile acids in liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) is involved in the regulation of bile acid metabolism. The activation of YAP disrupts the function of FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), a vital bile acid sensor. This disruption leads to bile acid overproduction, contributing to liver injuries and increasing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What treatments are available for liver disease linked to bile acid imbalance?
Treatment for liver disease caused by bile acid imbalance may involve targeting the FXR pathway or ensuring proper bile acid excretion. Pharmacological interventions that enhance FXR function or inhibit YAP’s repressor function have shown promise in reducing liver damage and curbing cancer progression.
What role do bile acids play in metabolic processes related to liver cancer?
Bile acids function beyond digestion; they also play a hormone-like role in metabolism. Their imbalance can lead to metabolic disruption within the liver, which is a contributing factor in the development of liver diseases and can enhance the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
How does liver disease treatment help prevent hepatocellular carcinoma?
Effective liver disease treatment focuses on correcting bile acid imbalances and enhancing metabolic pathways associated with liver function. By improving liver health and regulating bile production, these treatments can reduce the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and mitigate the effects of liver inflammation and fibrosis.
What are the implications of the Hippo/YAP pathway in liver cancer treatment?
The Hippo/YAP pathway is crucial in liver cancer as it regulates cell growth and bile acid metabolism. By targeting mechanisms within this pathway, such as enhancing FXR activity, researchers hope to develop new treatments that can prevent or halt the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) linked to bile imbalances.
Can enhancing FXR function improve outcomes in liver cancer patients?
Yes, enhancing FXR function is considered a promising approach in managing liver diseases related to bile imbalance. By promoting FXR activity, it may be possible to restore bile acid homeostasis, reduce liver inflammation, and prevent the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch Identified | The study identifies a key molecular switch that regulates bile, potentially offering new treatment avenues for liver cancer. |
| Bile’s Role in Digestion | Bile aids in fat digestion and also regulates metabolic processes due to bile acids acting similar to hormones. |
| Hippo/YAP Pathway | The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is crucial for cell growth regulation related to cancer. YAP inhibits FXR, a bile acid sensor. |
| Consequences of YAP Activation | YAP activation can lead to bile acid accumulation, fibrosis, inflammation, and progression towards liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s repressor activity or enhancing FXR function could mitigate liver damage and cancer progression. |
Summary
Bile imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A newly discovered molecular switch provides important insights into how bile acid regulation affects liver health. By unraveling the complex interactions between bile acids and the YAP signaling pathway, researchers can explore novel treatments that may help prevent liver cancer by restoring bile homeostasis. This discovery holds significant promise for future therapeutic strategies aimed at combating liver disease.
Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer: Key Insights Uncovered
Bile imbalance and liver cancer have become critical areas of research, particularly as studies highlight their intricate relationship. Recent findings indicate that an imbalance in bile acids, essential for fat digestion, can significantly escalate the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. By understanding the mechanisms behind bile acid metabolism and its regulation, particularly through the FXR receptor and the YAP signaling pathway, researchers are uncovering valuable insights that could revolutionize liver cancer treatment. This emerging connection between bile regulation and liver disease opens doors to innovative therapeutic interventions. As scientists continue to explore these pathways, they pave the way for potential strategies that could significantly impact patient outcomes in liver cancer care.
The disruption in bile acid equilibrium has emerged as a potential catalyst for severe liver conditions, intertwining with the pathology of liver malignancies. Investigating the role of bile acids in digestion reveals not only their digestive functions but also their hormonal regulation impact on liver health. Moreover, this field of study delves into the molecular underpinnings of liver cancer, especially focusing on key receptors and signaling pathways like FXR and YAP. Such insights are crucial, as they could lead to novel treatment modalities aimed at counteracting the effects of dysregulated bile functions. The implications of understanding this relationship underscore the need for continued research into liver disease and its treatment options.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance has emerged as a critical factor in the onset of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, essential for fat digestion and metabolism, play an intricate role in maintaining liver health. When the production and regulation of these bile acids are disrupted, it can lead to an accumulation in the liver, causing inflammation and, ultimately, liver cancer. Recent studies have spotlighted how specific molecular pathways, notably the YAP signaling pathway, influence bile acid metabolism and contribute to these disease processes.
In examining the interplay between bile acid homeostasis and liver cancer, it becomes evident that the FXR receptor is crucial. FXR is a nuclear receptor that regulates bile acid synthesis and excretion. Dysregulation, particularly through the action of YAP, has been shown to paralyze FXR’s function, leading to the overproduction of bile acids. This overproduction can create a toxic environment in the liver, promoting fibrosis and increasing the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Thus, understanding and targeting these molecular switches may provide new avenues for liver cancer treatments.
The Role of YAP in Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism
YAP, or Yes-associated protein, has been identified as a key regulator in the signaling pathways that govern bile acid metabolism. According to recent research, YAP’s activation plays a dual role—while it is commonly associated with promoting cell growth, it simultaneously disrupts the bile acid regulatory mechanisms. By repressing FXR, YAP leads to an imbalance of bile acids that can escalate the risk of liver injuries and facilitate the progression to liver cancer. The duality of YAP’s role underscores the need for targeted therapies that can mitigate its effects in the liver.
Researchers are exploring pharmacological strategies to enhance FXR function, seeking to reverse the negative effects of YAP activation. Treatments that either activate FXR or inhibit YAP’s repressive activities could restore bile acid balance and prevent liver disease progression. Early experimental models demonstrate that such interventions may significantly reduce liver damage and inhibit the precursors of hepatocellular carcinoma. Investigating YAP’s role in this context not only broadens the understanding of liver cancer but also points towards innovative treatment methodologies that leverage the body’s regulatory mechanisms.
Potential Treatment Strategies for Liver Cancer Through Bile Acid Modulation
The growing body of research highlights the importance of targeting bile acid metabolism as a viable therapeutic approach for treating liver cancer. By modulating the FXR receptor activity, researchers can potentially influence liver cell functions and mitigate the effects of bile acid overload. Interventions that enhance FXR activity have shown promise in experimental settings, where they help restore balance in bile acid production and protect against liver damage. This pharmacological approach could pave the way for new liver cancer treatments that are less invasive and more effective.
Moreover, promoting the excretion of bile acids through targeted therapies offers another pathway to combat liver cancer. Enhancing the function of bile acid export proteins, like BSEP, could reduce bile acid accumulation in the liver and lower inflammation levels. These strategies show potential in not only treating existing liver diseases but also in preventing the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma by addressing the root cause—bile imbalance. As research continues, understanding these intricate relationships will be crucial in developing comprehensive treatment protocols for patients at risk of liver cancer.
The Importance of Nutrient Sensing in Liver Health
A pivotal aspect of liver health is its capability to sense nutrients and adjust its metabolic responses accordingly. This nutrient sensing is crucial for maintaining metabolic homeostasis, and when disrupted, it can lead to various liver-related diseases, including liver cancer. Recent advancements demonstrate the significance of cell signaling pathways in this process, particularly those mediated by YAP. As YAP not only influences cell growth but also plays a critical role in regulating bile acid metabolism, its dysregulation can have cascading effects on liver health.
Understanding how nutrient sensing affects liver function could lead to innovative strategies for maintaining liver health and preventing disease progression. By exploring the relationships between nutrient availability, bile acid metabolism, and liver signaling pathways, researchers aim to uncover targets for pharmacological interventions. This multifaceted approach can provide robust methods for enhancing liver vitality, developing preventative care and treatment plans tailored to individual metabolic profiles.
Exploring FXR as a Target for Liver Cancer Treatment
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) has emerged as a promising target in the fight against liver cancer due to its central role in regulating bile acid metabolism. FXR is integral in maintaining the balance of bile acids in the liver, and its dysfunction is closely associated with liver diseases. Recent studies underline the potential of FXR activation as a therapeutic mechanism to counteract the harmful effects of bile acid accumulation, which, if left unchecked, can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
By enhancing FXR function through various pharmacological agents, researchers hope to restore normal bile acid homeostasis and reduce liver fibrogenesis. This approach not only addresses the immediate issues of bile imbalance but also provides a long-term strategy to mitigate cancer risk. The pursuit of FXR-focused therapies exemplifies a shift towards targeted treatments that aim to refine metabolic control and improve liver health, ultimately impacting outcomes for patients at risk of liver cancer.
The Role of Cell Signaling in Liver Disease Progression
Cell signaling pathways play a fundamental role in the progression of liver diseases, particularly liver cancer. Pathways such as Hippo/YAP have been shown to regulate essential cellular processes, influencing growth and metabolism within the liver. Disruptions in these signaling cascades can lead to adverse effects on liver function and increased susceptibility to diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these pathways provides crucial insights into the mechanisms underlying liver disease progression.
Research into cell signaling not only enhances our understanding of liver biology but also opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions. By identifying specific signaling proteins and their functions, scientists aim to develop targeted therapies that can interrupt the pathological processes involved in liver disease. Progress in this area could lead to innovative treatments that effectively combat liver cancer and enhance patient outcomes through more precise and tailored approaches.
Investigating the Interplay Between Bile Acids and Cancer Metabolism
The interplay between bile acids and cancer metabolism underscores the complexity of liver biology and the pathophysiology of liver cancer. Bile acids serve not only digestive functions but also influence metabolic pathways that can either promote or inhibit cancer progression. Recent findings suggest that an imbalance in bile acids can trigger metabolic switches that favor tumor development, particularly in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these dynamics is vital for developing effective treatment strategies.
By exploring how bile acids interact with cancer metabolism, researchers can identify novel therapeutic targets that may disrupt the tumor-promoting environments created by bile acid dysregulation. This multifaceted approach highlights the necessity of integrated research efforts that encompass both metabolic and cellular aspects of liver cancer, promoting a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and potential intervention strategies.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Treatment Research
As the understanding of liver cancer mechanisms deepens, future directions in treatment research are becoming increasingly clear. The focus on bile acid metabolism and its regulation through pathways such as YAP and FXR represents a significant frontier in combating liver diseases. Researchers are now poised to investigate innovative drug formulations that target these pathways, which may lead to breakthroughs in therapeutic interventions. The promise of personalized medicine, based on individual metabolic profiles, could further enhance the efficacy of these treatments.
Continued collaboration between biologists, pharmacologists, and clinicians is essential to translate these laboratory findings into viable clinical treatments. As research progresses, the commitment to uncovering the links between bile imbalance and liver cancer will undoubtedly yield new strategies that can improve prognosis and quality of life for patients. With a focus on understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms, the future of liver cancer treatment appears promising, laying the groundwork for advanced therapies that tackle the disease at its root.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
A notable connection exists between bile imbalance and liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid production can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are risk factors for HCC. The imbalance triggers responses that can result in tumor formation through mechanisms such as the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway.
How does bile acid metabolism relate to liver cancer treatment?
Bile acid metabolism is crucial in liver cancer treatment strategies. Research indicates that disturbances in bile acid levels may worsen liver conditions, including HCC. By targeting components like the FXR receptor to restore bile acid balance, new therapeutic options may emerge that can inhibit cancer progression and improve liver health.
What role does the FXR receptor play in hepatocellular carcinoma?
The FXR receptor is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. In the context of hepatocellular carcinoma, FXR dysfunction—often caused by YAP signaling—can lead to increased bile acid production that contributes to liver fibrosis and cancer. Therapies aimed at enhancing FXR function may provide new avenues for liver cancer treatment.
Can YAP signaling pathway influence bile imbalance and liver cancer development?
Yes, the YAP signaling pathway significantly influences bile imbalance and liver cancer development. YAP has been found to act as a repressor of FXR, which disrupts bile acid metabolism. This disruption can lead to an overproduction of bile acids, inflammation, and ultimately the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are the potential pharmacological solutions for liver cancer related to bile imbalance?
Potential pharmacological solutions for liver cancer related to bile imbalance include drugs that enhance FXR function, inhibit YAP’s repressive role, or promote bile acid excretion. Targeting these pathways may halt the detrimental cycle of bile acid accumulation, reducing liver damage and cancer progression.
How does liver cancer treatment focus on bile acid metabolism?
Liver cancer treatment increasingly focuses on bile acid metabolism because imbalances can aggravate liver disease. By manipulating bile acid levels and ensuring proper metabolism through mechanisms involving FXR and YAP, researchers hope to develop targeted therapies that mitigate liver cancer progression.
What is the significance of the research on bile imbalance and liver cancer?
The significance of recent research on bile imbalance and liver cancer lies in the identification of molecular pathways that link bile acid dysregulation to tumor development. Understanding these connections can inform novel treatment strategies aimed at restoring bile acid homeostasis and potentially preventing or managing hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer |
| Bile acids are essential for fat digestion and regulate metabolic processes. |
| Disruption in bile acid regulation can lead to liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway plays a crucial role in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer progression. |
| YAP activates at FXR, disrupting bile acid homeostasis causing liver inflammation and fibrosis. |
| Targeting YAP activity or enhancing FXR could provide new treatment avenues for liver cancer. |
Summary
Bile imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research has identified critical pathways involved in bile acid regulation, which are essential for maintaining liver health. Disruptions in these processes can lead to liver injury and cancer progression. By focusing on the YAP pathway and its interaction with bile acid metabolism, new therapeutic strategies can be developed to prevent or treat liver cancer effectively.